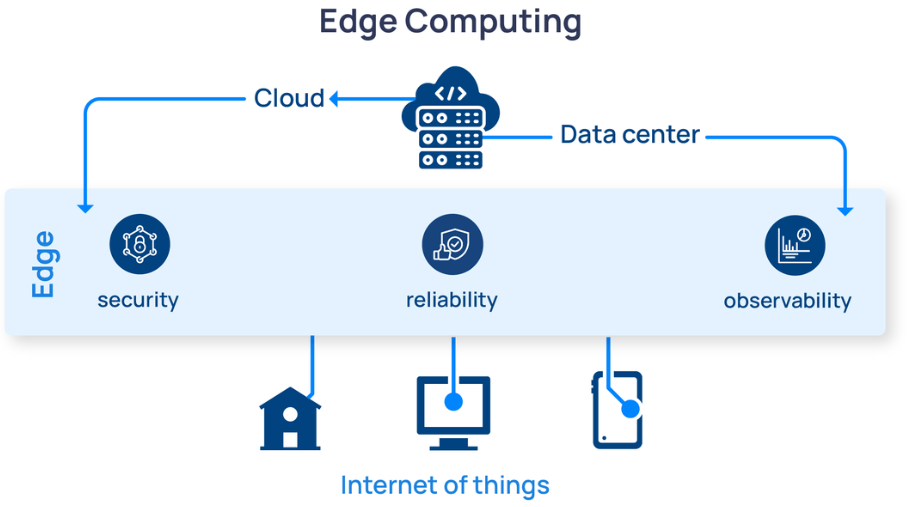
With the exponential growth of connected devices, Edge computing is becoming a game changer. Edge computing is a model that processes data near the network edge where data is generated. It addresses the issues of latency, bandwidth, and data privacy more effectively than centralized cloud architectures. However, managing and orchestrating applications and services at the Edge is no easy task. Robust, lightweight, and reliable tools are needed — a challenge some open source tools are prepared to tackle. By combining Rancher Prime, Buoyant’s Linkerd, RKE2, and K3s, users get a state-of-the-art, highly secure, highly performant solution for unique edge requirements.
Introducing the architecture
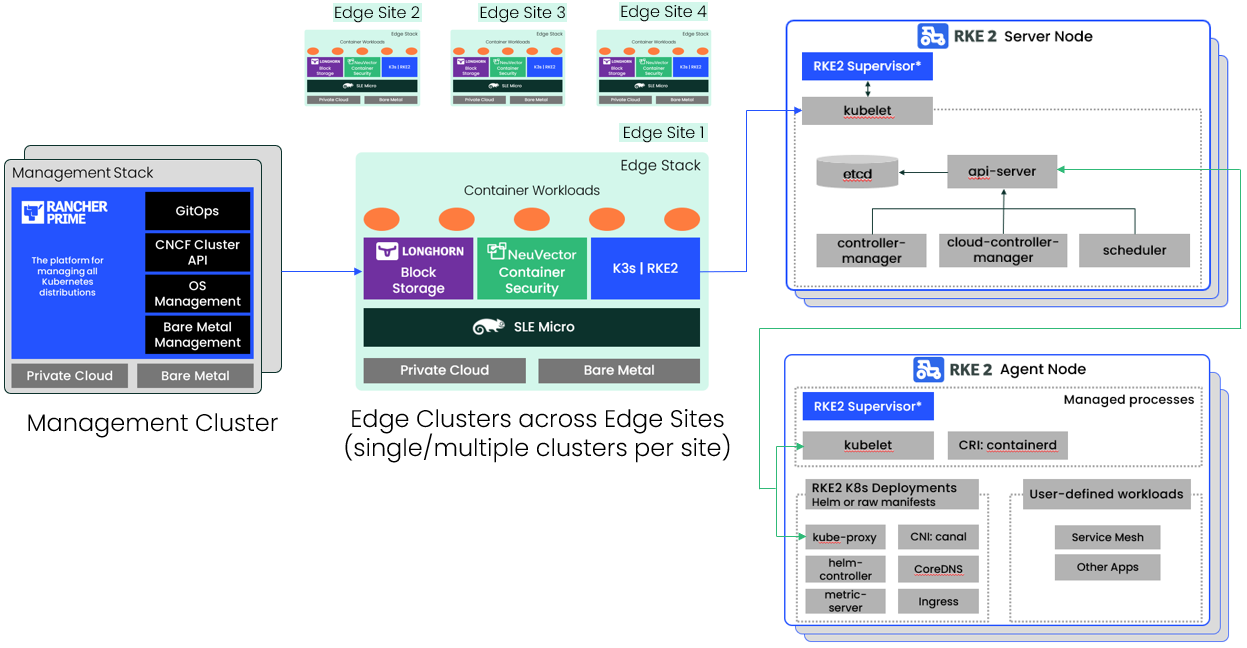
Before we get into the "how," let's introduce the edge computing stack and examine why these tools work so well together for an edge computing scenario. If you are running Rancher, we recommend combining Rancher Prime, Buoyant's Linkerd, RKE2, and K3s (for an overview of what each piece does, please refer to the table below).
Why this stack for edge computing? First and foremost, they integrate seamlessly, which will save you a lot of headaches. Additionally, Linkerd and RKE2 significantly improve security, while Linkerd provides an additional layer of reliability. This stack is lightweight and resource efficient, making it ideal for resource-constrained environments. And lastly, all these tools focus on operational simplicity. And when it comes to edge computing, that is incredibly important. With multiple disparate devices, you need a unified way to operate them all.
| Project Name | What it is | Why for the edge? |
|---|---|---|
| Buoyant’s Linkerd | Open-source, security-first service mesh for Kubernetes | Provides security, reliability, and observability without any code changes. Is ultra-lightweight and easy to install with a small runtime footprint (this is key in edge computing where managing communication must be efficient) |
| Rancher Prime | Open-source multi-cluster Kubernetes orchestration platform | Flexible and compatible with any CNCF Kubernetes distribution, including K3s and RKE2, Rancher Prime proactively monitors cluster health and performance. |
| RKE2 | CNCF-certified Kubernetes distribution optimized for air-gapped, offline, or edge environments deployed at the core or near the edge. | Fully CNCF-certified, RKE2 improves security and simplicity of your Kubernetes deployment. It is designed to be secure, reliable, and lightweight, ideal for general-purpose computing and near-edge use cases. |
| K3s | CNCF-certified ultra-lightweight Kubernetes distribution providing the best choice for clusters running at the edge. | Ideal for edge applications, allowing for simple deployment and management while still fully CNCF-certified. It is ultra-lightweight and optimized for resource-constrained environments and functions even in remote and disconnected areas. |
Security, reliability, and observability are all critical concerns for edge computing, and it’s therefore important to choose an architecture that helps, rather than hinders, accomplishing these goals. An effective architecture will be simple to deploy and operate, using technologies in ways that play to their strengths, as described above. With Rancher and Linkerd, we can adopt an extremely simple architecture that nevertheless brings an enormous amount of functionality to the table:
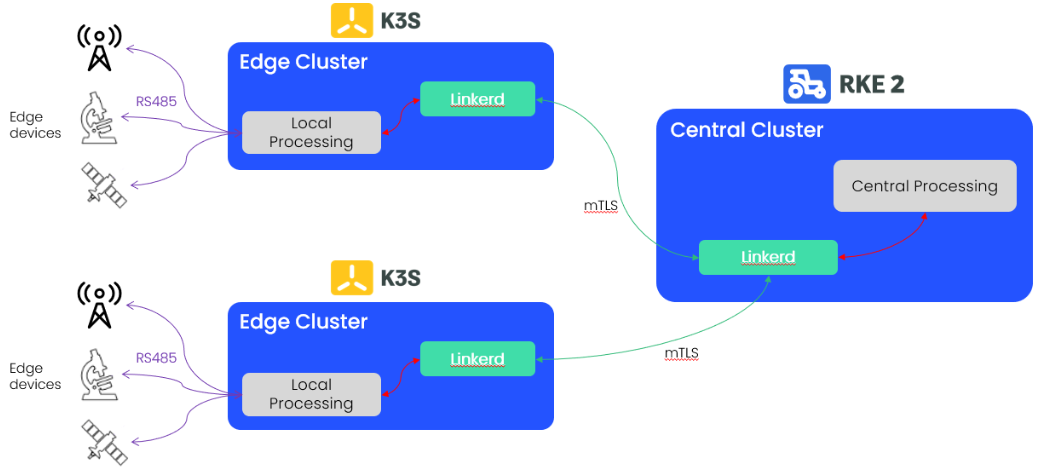
Here, our instruments (on the left of the diagram) are connected to IoT “gateway” systems running Linux. By deploying k3s clusters with Linkerd all the way out on the edge gateways, we can use Linkerd’s secure multicluster capabilities to extend the secure service mesh all the way from the central cluster (shown on the right, running RKE) to the edge gateways themselves.
These tools all integrate seamlessly, providing a secure, reliable, observable edge platform that is lightweight and resource efficient. Now let's explore why we believe these technologies are a perfect match for the edge.
Why Rancher and Buoyant's Linkerd?
Seamless Integration
One of the most significant advantages of combining Rancher Prime, Linkerd, RKE2, and K3s is their compatibility. These tools are designed to work hand-in-hand, providing a seamless experience. Rancher provides the overarching platform to manage your Kubernetes clusters, including RKE2, K3s, EKS, AKS, GKE, etc. And Linkerd easily integrates with any Kubernetes distribution, adding a service mesh layer to your Rancher-managed clusters.
Reliability and Robustness
Linkerd adds a layer of reliability and robustness to your Kubernetes clusters by providing traffic splitting, retries, and timeouts capabilities for your applications. With its fault-tolerance feature, Linkerd ensures your applications continue running smoothly, even in the event of a network failure.
RKE2 takes Kubernetes security to the next level. It includes several enhancements like CIS benchmark compliance, security by default, and defense in depth. These features, along with Linkerd's ability to automate mutual TLS for all service-to-service communication, provide a secure environment for your Edge computing needs.
Lightweight and Resource Efficient
Edge environments often have limited resources. K3s is designed explicitly for such situations. It is a fully compliant Kubernetes distribution with a significantly smaller footprint, consuming less than half the memory of a typical Kubernetes installation. This lightweight nature extends to Linkerd as well, which maintains a small runtime footprint, making it an ideal service mesh for Edge environments.
Comprehensive Observability
With numerous devices and applications running in various locations, clearly understanding their performance and issues is vital. The Rancher Prime, Linkerd, RKE2, and K3s stack addresses that by providing comprehensive observability capabilities.
Rancher enables users to monitor and manage clusters from a unified interface, regardless of where they are deployed. With built-in monitoring and alerting tools, users get detailed insight into cluster health, allowing for quick identification and resolution of potential issues. Linkerd provides deep real-time data into your applications' performance and includes features such as request volume, success rates, and latency distributions for all meshed services. Users get a more granular level of observability into microservices communication, which is crucial in Edge computing scenarios where the network is notorious for being unstable and latency-sensitive. Linkerd also automatically adds mTLS to all service-to-service communication, adding security with no code changes, which is particularly valuable in Edge computing.
Operational Simplicity
When it comes to Edge computing, operational simplicity is key. Edge environments involve managing numerous devices, often spread across multiple geographical locations, making traditional management methods impractical. Rancher simplifies Kubernetes cluster management with an intuitive user interface and robust API. Rancher allows users to manage all their Kubernetes clusters from a single control point, whether in the cloud, data center, or Edge environments. This unified approach simplifies operations and reduces the complexity of managing multiple clusters.
The Linkerd service mesh requires minimal configuration and comes with zero-config features such as load balancing, retries, timeouts, and more. With no time-consuming setup, developers have more time to build business logic. That being said, edge devices will require some initial setup work and configuration. Due to their resource limitations, these devices typically require deployment optimization to ensure they run efficiently.
Linkerd Architecture:
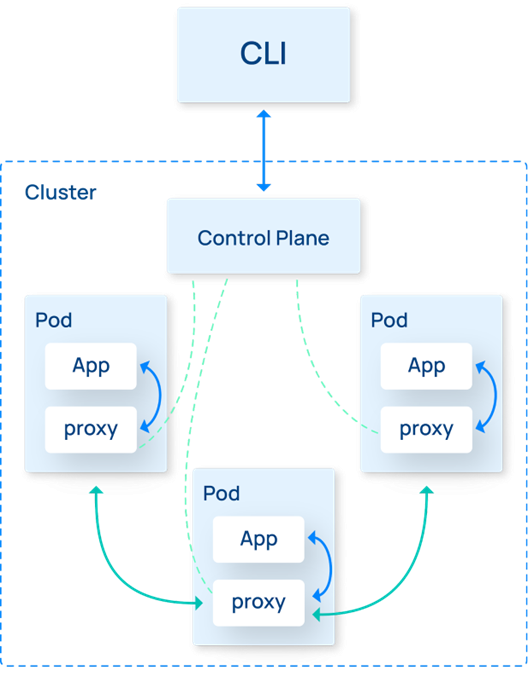
The Linkerd architecture is fairly simple. The Linkerd control plane manages Linkerd’s operation; it also has a CLI that the user can use to configure, and examine, the mesh. Application Pods that are part of the mesh have the ultra-fast, ultra-lightweight Linkerd proxy, purpose-built in Rust, injected into them as a sidecar container. Once the proxy is injected, all application communication goes through the proxy, which manages mTLS, workload authentication and authorization, retries, circuit breaking, metrics collection, and much more. Having these critical features uniformly applied across the entire application at the platform level eliminates the need to change the application itself, meaning that the application developers are free to focus on the business needs of the application rather than on the complexities of the network.
Edge computing use case examples
Industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, transportation, retail, and energy are all increasingly taking advantage of edge computing to optimize their operations. Let's look at some examples. But keep in mind that the stack is vertical agnostic. The role of Rancher, Linkerd, K3s, and RKE2 is always the same. The examples below put them in industry-specific context.
| Industry Use Case | Retail Industry - Point of Sale (POS) Systems | Manufacturing - Predictive Maintenance | Healthcare - Remote Patient Monitoring | Transportation - Fleet Management | Summing it up |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specific challenge | In retail environments the people setting up and maintaining the physical devices are more likely to be store managers than technicians. This leads to fragile physical systems. | Predictive maintenance is often critical. Manufacturing equipment sensors send data to the central system that predicts potential equipment failures. | In remote patient monitoring scenarios, patient health data is often collected by various devices and sent to a central system for analysis and monitoring. | Modern fleet management uses real-time vehicle data for route optimization, improved fuel efficiency, and predictive maintenance. | Edge devices must process and analyze data in real-time to ensure business continuity (manufacturing, transportation), save lives (healthcare), or save money (retail). |
| Rancher | Multi-cluster management enables easy containerized app deployment and management across stores in various geo locations. | Manages edge deployments, providing a central point of control for all the clusters running on the factory floor. | Helps manage the deployment of these applications across various devices and locations, ensuring uniformity and ease of management. | Manages edge deployments across various vehicles, providing a central point of control for all the clusters. | Centralized management of distributed containerized apps on the edge. |
| Linkerd | Guarantees secure, reliable communication between store POS systems and cloud-based central inventory management systems. Provides real-time inventory updates and transaction processing. Seamlessly merges multiple clusters into a single secure mesh. | Guarantees secure, reliable communication between sensors and the applications processing the data. Seamlessly merges multiple clusters into a single secure mesh. | Guarantees secure and reliable communication between patient devices and central health monitoring system. Seamlessly merges multiple clusters into a single secure mesh. | Guarantees secure and reliable communication between the onboard devices and the central fleet management system. Seamlessly merges multiple clusters into a single secure mesh. | Guarantees secure and reliable communication from the edge to the central processing and analysis system. |
| RKE2 | For store backend systems, ensuring reliable and secure operation of the POS system. | Provides secure, reliable Kubernetes runtime for the central systems processing and analyzing the sensor data. | Provides secure, reliable Kubernetes runtime for central health monitoring systems, so patient data is processed accurately and securely. | Provides secure, reliable Kubernetes runtime for central fleet management systems, ensuring real-time fleet data is processed accurately and securely. | Provides secure, reliable Kubernetes runtime for the central system. |
| K3s | Efficiently deploy and manage containerized apps across multiple stores. | Run data processing apps at the edge, close to data source, reducing latency and network load. | Efficiently processes data at the edge, reducing latency and ensuring timely alerts in case of any health anomalies. | Processes data at the edge, providing real-time insights and reducing network load. | Efficiently processes data at the edge. |
Edge Computing stack:
Accelerate time-to-value with the Rancher and Buoyant teams
As Edge computing use cases rapidly expand, the Rancher Prime, Linkerd, RKE2, and K3s toolkit offers a state-of-the-art, highly secure, and highly performant to these unique challenges. It provides organizations and developers with the tools and strategies they need to deliver fast, reliable performance and robust, secure communication between microservices and applications, all while efficiently managing and orchestrating Kubernetes clusters.
Practical use cases showcase how these open source tools synergize to create robust, efficient, and flexible Edge computing solutions. From Retail industry POS systems to remote patient healthcare monitoring, this stack has clear advantages. An easy integration streamlines your Edge computing implementation, and enables you to process data at the Edge, while ensuring reliable and secure data transfer, reducing latency, and providing scalability and flexibility.
As with any implementation, there are some challenges, however. The initial setup and configuration on the edge can be complex. A deep understanding of these tools and Kubernetes is required. If you need help and want to accelerate your time-to-value, the Buoyant and SUSE teams can help. Reach out, and let's chat!
Contact the Buoyant team at: https://buoyant.io/contact
Contact the SUSE team at: https://www.suse.com/contact/
To sum it up, combining Rancher Prime, Linkerd, RKE2, and K3s delivers a robust, observable, and easy-to-manage Edge computing solution. Organizations gain a powerful set of capabilities to improve edge computing performance and tackle the complexities and challenges of managing edge environments. As edge computing applications across industries continue to proliferate, these tools will play an increasingly critical role in shaping the future of how we process, manage, and utilize data in an increasingly decentralized world.
